Comets - these are cold bodies, and we see them only because the gases in a coma and the tail glow as a result of the reflection of sunlight from solid particles. Comets are permanent members of the solar system family, linked to the sun by gravity. Comets are believed to have originated from the same material from which the solar system was formed, but this is the remaining debris, so to speak, from the formation of planets. But according to the latest data, at an early stage of the formation of the solar system. It is the fact that they are believed to be composed of original, unchanging material makes them extremely interesting to study, as it allows you to learn about the conditions in the early stages of the solar system. They are real.
The size and shape of comets
Comets are very small in size compared to planets planets. Their average diameter is usually 750 meters to 20 kilometers. AT recent times more distant comets have been found, possibly up to 300 kilometers or more in diameter, but these sizes are still small compared to planets. The planets are spherical, usually slightly convex at the equator. Comets have irregular shape... Recent evidence suggests that comets are very fragile. Their tensile strength is only about 1000 dynes / cm ^ 2. You can take a large piece of comet material and tear it apart with both hands, like a poorly compacted snowball.
Comet orbits
Comets, of course, must obey the same universal laws of motion as all other objects. The orbits of the planets around the Sun are almost circular, but rather elongated. Their farthest point from the Sun (aphelion) is near the orbit of Jupiter, the closest point (perihelion) is much closer to the Earth. For example, y, aphelion is beyond the orbit of Neptune.
Other comets come from more distant regions of the solar system and take thousands or even hundreds of thousands of years to complete one complete revolution around the sun. If a comet approaches close to Jupiter, it is subject to its strong gravitational influence and the comet's orbit sometimes changes radically. This is an example of what happened to
A comet is a celestial nebulous object with a characteristic bright clot nucleus and a glowing tail. Comets are composed primarily of frozen gases, ice, and dust. Therefore, we can say that a comet is such a huge dirty snowball flying in space around the Sun in a very elongated orbit.
 comet Lovejoy, photo taken on the ISS
comet Lovejoy, photo taken on the ISS
Where do comets come from?
Most comets come to the Sun from two places - the Kuiper belt (the asteroid belt behind Neptune) and the Oort cloud. The Kuiper Belt is the asteroid belt beyond the orbit of Neptune, and the Oort Cloud is a cluster of small celestial bodies at the edge of the Solar System, which is farthest from all planets and the Kuiper belt.
How do comets move?
Comets can spend millions of years somewhere very far from the Sun, not bored at all among their fellows in the Oort cloud or Kuiper belt. But one day, there, in the farthest corner of the solar system, two comets may accidentally pass next to each other or even collide. Sometimes, after such a meeting, one of the comets may begin to move towards the Sun.
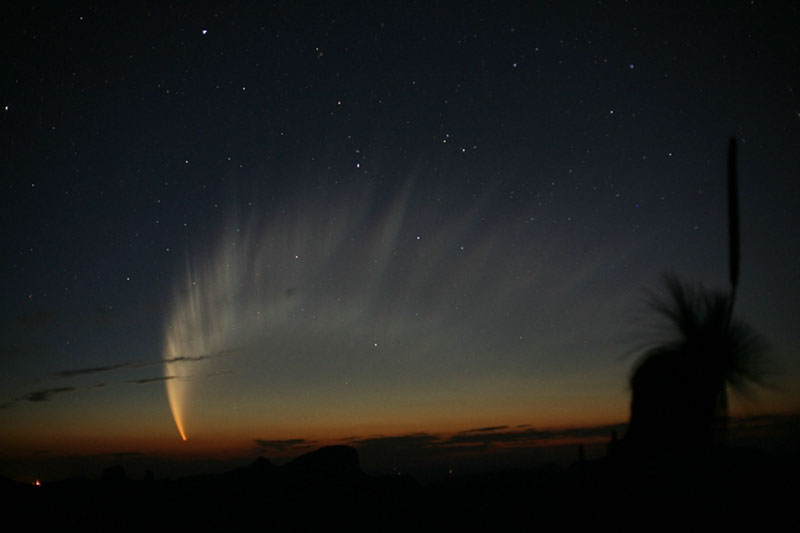

The sun's gravitational pull will only accelerate the comet's motion. When it gets close enough to the Sun, the ice will begin to melt and evaporate. At this moment, the comet will have a tail, consisting of dust and gases, which the comet leaves behind. The dirty snowball begins to melt, turning into a beautiful "heavenly tadpole" - a comet.
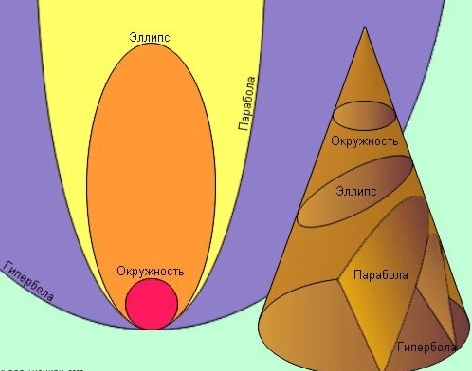
The fate of the comet depends on which orbit it starts to move. As you know, all celestial bodiescaught in the gravitational field of the Sun can move either in a circle (which is possible only theoretically), or along an ellipse (this is how all planets, their satellites, etc. move) or along a hyperbola or parabola. Imagine a cone, and then mentally cut a piece from it. If you cut the cone at random, either a closed figure - an ellipse, or an open curve - a hyperbola, will most likely come out. In order to get a circle or a parabola, it is necessary that the section plane be oriented strictly definitely. If the comet moves in an elliptical orbit, it means that one day it will return to the Sun again. If the orbit of the comet becomes a parabola or hyperbola, then the attraction of our star will not be able to hold the comet, and humanity will see it only once. Having flown past the Sun, the wanderer will go away from the solar system, wagging her tail goodbye.
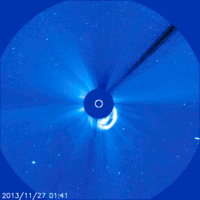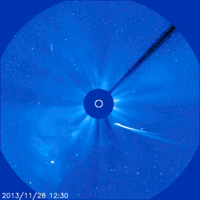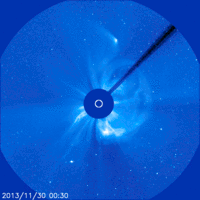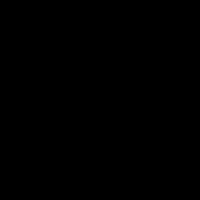 here you can see that at the very end of the survey, the comet falls apart into several parts
here you can see that at the very end of the survey, the comet falls apart into several parts
It often happens that comets do not survive travel to the Sun. If the mass of a comet is small, then it can completely evaporate in one flight past the Sun. If the material of the comet is too loose, then the force of gravity of our star can tear the comet apart. This has happened more than once. For example, in 1992, the Shoemaker-Levy comet, flying past Jupiter, disintegrated into more than 20 fragments. Jupiter then flew hard. The debris of the comet crashed into the planet, causing violent atmospheric storms. And more recently (November 2013) Comet ison could not stand its first flight past the Sun, and its core disintegrated into several fragments.

How many tails does a comet have?
Comets have multiple tails. This is because comets are not only made of frozen gases and water, but also dust. When moving towards the Sun, the comet is constantly blown by the solar wind - a stream of charged particles. It has a much stronger effect on light gas molecules than on heavy dust particles. Because of this, the comet has two tails - one dusty, the other gas. The gas tail is always directed exactly from the Sun, the dust tail twists slightly along the trajectory of the comet.

Sometimes comets have more than two tails. For example, a comet may have three tails, for example, if at some point from the comet's nucleus, a large number of dust particles, they form a third tail, separate from the first dust and the second gas.
What if the Earth flies through the comet's tail?
And nothing will happen. The comet's tail is just gas and dust, so if the Earth flies through the comet's tail, then the gas and dust will simply collide with earthly atmosphere and either burn up or dissolve in it. But if a comet crashes into the Earth, then we may all have a hard time.
Presumably, long-period comets fly to us from the Oort Cloud, which contains millions of cometary nuclei. Bodies located on the outskirts of the solar system, as a rule, consist of volatile substances (water, methane and other ice) that evaporate when approaching the Sun.
On this moment discovered more than 400 short-period comets. Of these, about 200 were observed in more than one perihelion pass. Many of them belong to the so-called families. For example, about 50 of the shortest-period comets (their complete revolution around the Sun takes 3-10 years) form the Jupiter family. Slightly smaller than the family of Saturn, Uranus and Neptune (the latter, in particular, includes the famous Halley's comet).
Comets emerging from the depths of space look like foggy objects, behind which stretches a tail, sometimes reaching a length of millions of kilometers. The comet's nucleus is a body of solid particles and ice, enveloped in a foggy shell called a coma. A nucleus with a diameter of several kilometers can have a coma around it 80 thousand kilometers across. Streams sun rays knock gas particles out of the coma and throw them back, pulling them into a long smoky tail that trails behind it in space.
The brightness of comets is highly dependent on their distance from the Sun. Of all comets, only a very small fraction are close enough to the Sun and Earth to be seen with the naked eye. The most prominent of these are sometimes referred to as "Big Comets".
Comet structure
Comets move in elongated elliptical orbits. Note the two different tails.
As a rule, comets consist of a "head" - a small bright clot-nucleus, which is surrounded by a light foggy shell (coma), consisting of gases and dust. In bright comets, as they approach the Sun, a "tail" is formed - a weak luminous band, which, as a result of light pressure and the action of the solar wind, is most often directed in the opposite direction from our star.
The tails of celestial comet wanderers differ in length and shape. For some comets, they stretch across the sky. For example, the tail of a comet that appeared in 1944 [ clarify], was 20 million km long. And comet C / 1680 V1 had a tail stretching for 240 million km.
The tails of comets do not have sharp outlines and are practically transparent - the stars are clearly visible through them - as they are formed from extremely rarefied matter (its density is much less than the density of the gas released from a lighter). Its composition is varied: gas or the smallest specks of dust, or a mixture of both. The composition of most dust grains is similar to asteroid material. solar system, which became clear as a result of the study of comet Wild (2) by the spacecraft "Stardust". In fact, this is "visible nothing": a person can observe the tails of comets only because gas and dust glow. In this case, the glow of the gas is associated with its ionization ultraviolet rays and streams of particles ejected from the solar surface, and dust simply scatters sunlight.
The theory of comet tails and shapes was developed at the end of the 19th century by the Russian astronomer Fedor Bredikhin (-). He also belongs to the classification of cometary tails, which is used in modern astronomy.
Bredikhin proposed to classify comet tails to the main three types: straight and narrow, directed directly from the Sun; wide and slightly curved, deviating from the Sun; short, strongly deviated from the central star.
Astronomers explain so various forms comet tails as follows. The particles that make up comets have different compositions and properties and respond differently to solar radiation... Thus, the paths of these particles in space "diverge", and the tails of space travelers acquire different shapes.
Comets near
What are the comets themselves? Astronomers got an exhaustive picture of them thanks to the successful "visits" to Halley's comet of the spacecraft "Vega-1" and "Vega-2" and the European "Giotto". Numerous instruments installed on these spacecraft transmitted to the Earth images of the comet's nucleus and various information about its shell. It turned out that the nucleus of Halley's comet consists mainly of regular ice (with small inclusions of carbon dioxide and methane ices), as well as dust particles. They form the shell of the comet, and as it approaches the Sun, some of them - under the pressure of the sun's rays and the solar wind - pass into the tail.
The dimensions of the nucleus of Halley's comet, as scientists correctly calculated, are equal to several kilometers: 14 - in length, 7.5 - in the transverse direction.
The nucleus of Halley's comet has an irregular shape and rotates around an axis that, as the German astronomer Friedrich Bessel (-) assumed, was almost perpendicular to the comet's orbital plane. The rotation period turned out to be 53 hours - which again agreed well with the calculations of astronomers.
Notes
Comet researchers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
See what "Comets" are in other dictionaries:
Celestial bodies that occasionally appear in the solar system. They are light nebulae with a brilliant core inside; most often a light trail, or, as it is called, a tail, stretches behind them; he is always facing the opposite sun ... ... Dictionary foreign words Russian language
- (Greek, singular kometes, literally long-haired) small bodies of the solar system with extended (up to hundreds of millions of kilometers) non-stationary atmospheres. From other small bodies K. also differ in physical. chem. and orbital characteristics. It is precisely ... ... Physical encyclopedia
- (Comet) celestial bodies in the form of a foggy spot with a more or less bright core in the middle; most of them are accompanied, in addition, by a rather light hazy stripe called the tail of a comet. Some of them appear on the corpus ... ... Marine dictionary
comets - The celestial bodies of the solar system, moving in highly elongated orbits, consisting of an ice core and a gas "tail" stretched for a million km. [Dictionary of geological terms and concepts. Tomsk State University] Topics ... ... Technical translator's guide
- (from the Greek kometes a star with a tail, a comet; literally long-haired) bodies of the solar system, which look like nebulous objects, usually with a light lump in the center and a tail. General information about comets. K. are observed when ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
- (from the Greek komētēs, literally long-haired), the bodies of the Solar system move in highly elongated orbits, at considerable distances from the Sun they look like faintly glowing oval-shaped specks, and as they approach the Sun they appear ... ... encyclopedic Dictionary
The material basis of comets as small bodies of the solar system is a solid core. Most likely, cometary nuclei are a conglomerate of water ice and ice gases with fine cosmic dust. As it approaches the Sun from the surface of the comet, the process of rapid evaporation of all kinds of volatiles begins. This is how a giant gas plume, illuminated by the rays of the Sun, appears, which stretches for tens of millions of kilometers behind the cometary nucleus.
Comet Hale - Bopp
People from ancient times have observed strange luminaries with long foggy tails. They saw in them frightening, then happy signs. It is now known that comet nuclei are composed of ice and rock, and tails occur when the Sun evaporates ice from the surface of the nucleus. Comet Hale-Bopp has become the most observed comet of the 20th century. It was discovered in 1995, two years before the passage of perihelion, the point of maximum approach to the Sun, and immediately began to predict very high brightness. In May 1996, the comet could be observed with the naked eye. In March - April 1997, its brightness exceeded one magnitude, and only at the end of the year it ceased to be visible without the help of optics, shining in the sky for 18 months - more than all other known comets.
If nothing happens to the comet in space, it will return in about 4390.
Comet ISON
The unpredictability of comets often plays a cruel joke with scientists and the public, eager for sensations. Comet ISON was discovered in 2012 by astronomers Vitaly Nevsky (Belarus) and Artem Novichonok (Russia). In November 2013, she was supposed to approach the Sun. Based on what was known about the comet, some scientists suggested that it could become very bright, equal in brightness to full moon, and visible in the daytime sky. Since the beginning of 2013, doubts arose about the justification of these predictions - the comet did not gain brightness. However, the media were already trumpeting about the “comet of the century”.

In November ISON nevertheless began to flare up in last weeks before approaching the sun, it became visible with the naked eye, although it was difficult to detect it against the background of the dawn. It was assumed that, like some of its predecessors, the comet will arrange a "show" after the passage of perihelion. However, on November 28, after flying only 1 million km from the surface of the Sun, it collapsed. Now in its orbit only fine particles dust.
Comet McNaught
Comets are very unpredictable stars. It is rather difficult to predict their brightness and behavior when approaching the Sun.
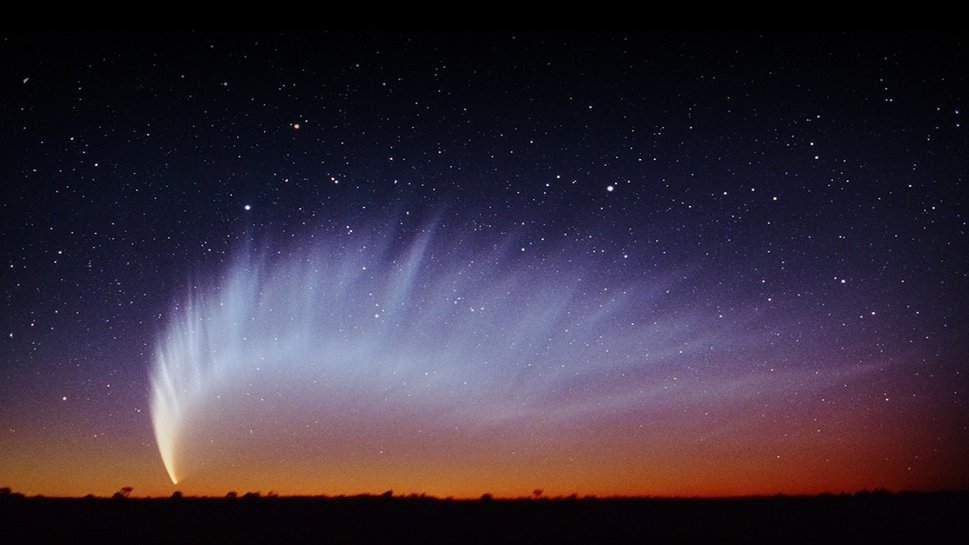

This comet was discovered in 2006 and named after its discoverer Robert McNaught. It was assumed that it would be visible to the naked eye, but not reach high brightness. As it approached the Sun, the comet began to gain brilliance at a much faster rate than scientists predicted. In January 2007, its brightness exceeded the brightness of Venus for some time. The comet made a spectacular show for the inhabitants of the southern hemisphere of the Earth, spreading a huge curved tail across the sky.
The orbits of comets are highly elongated conical sections: ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas. It is not uncommon for a comet to approach the Sun once and, having rounded it, flies away forever. Comet McNaught also moved in such an orbit. However, the attraction of the Sun and the planets changed it, now it will revolve around the Sun with a colossal period of about 92,000 years.
Halley's comet
The most famous comet in the solar system is undoubtedly Halley's comet. She played in the history of astronomy, and celestial mechanics great role and is closely related to the discovery of the law of universal gravitation. The fact is that Isaac Newton's colleague and friend, the astronomer and mathematician Edmund Halley, was the author of the first catalog of all previously observed comets. While processing the data, Halley drew attention to a strange pattern: three comets appeared with a clear periodicity of 76 years, moving almost along the same trajectory. Naturally, the thought immediately dawned on him that it could be the same celestial body. On the basis of his hypothesis, Halley predicted the next appearance of a strange planet - and was not mistaken, and Newton used his calculations to build his theory of gravity, which was later called the law of universal gravitation.
The comets of the solar system have always interested researchers outer space... The question of what these phenomena are, worries people who are far from studying comets. Let's try to figure out what this celestial body looks like, whether it can affect the life of our planet.
The content of the article:
A comet is a celestial body formed in Space, the dimensions of which reach the scale of a small settlement. The composition of comets (cold gases, dust and rock debris) makes this phenomenon truly unique. The comet's tail leaves a plume that is estimated at millions of kilometers. This spectacle fascinates with its grandeur and leaves more questions than answers.
The concept of a comet as an element of the solar system

To understand this concept, one should start from the orbits of comets. Quite a few of these cosmic bodies pass through the solar system.
Let's consider in detail the features of comets:
- Comets are the so-called snowballs that pass through their orbit and contain dusty, rocky and gaseous clusters.
- The heating of a celestial body occurs during the period of approaching the main star of the solar system.
- Comets do not have satellites that are characteristic of planets.
- Formation systems in the form of rings are also not typical for comets.
- It is difficult and sometimes unrealistic to determine the size of these celestial bodies.
- Comets don't support life. However, their composition can serve as a certain building material.
Features of the structure of comets
The description of the comet can be divided into the characteristics of the nucleus, coma, and tail of the object. This suggests that the studied celestial body cannot be called a simple construction.
Comet nucleus
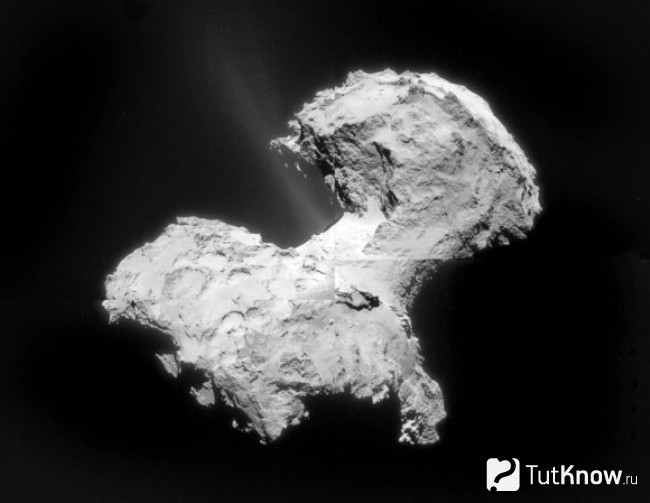

Almost all of the comet's mass is contained in the nucleus, which is the most difficult object to study. The reason is that the core is hidden even from the most powerful telescopes by the matter of the luminous plane.
There are 3 theories that consider the structure of the comet nucleus in different ways:
- Dirty Snow Theory... This assumption is the most widespread and belongs to the American scientist Fred Lawrence Whipple. According to this theory, the solid section of the comet is nothing more than a combination of ice and fragments of meteorite composition. According to this specialist, old comets and bodies of a younger formation are distinguished. Their structure is different due to the fact that more mature celestial bodies repeatedly approached the Sun, which melted their original composition.
- The core is made of dusty material... The theory was voiced at the beginning of the 21st century thanks to the study of the phenomenon of American space station... This intelligence indicates that the core is a very loose dusty material with pores occupying most of its surface.
- The kernel cannot be a monolithic structure... Further, hypotheses diverge: they imply a structure in the form of a snow swarm, blocks of rock-ice accumulations and a meteorite pile up due to the influence of planetary gravitations.
Comet coma

Together with the nucleus, the head of the comet forms a coma, which is a fog-like shell light color... The trail of such a component of the comet stretches for a rather long distance: from one hundred thousand to almost one and a half million kilometers from the base of the object.
Three levels of coma can be identified, which look like this:
- Interior chemical, molecular and photochemical composition... Its structure is determined by the fact that in this area the main changes occurring with the comet are concentrated and most active. Chemical reactions, decay and ionization of neutrally charged particles - all this characterizes the processes that take place in the internal coma.
- Coma of radicals... Consists of active in their own way chemical nature molecules. In this area, there is no increased activity of substances, which is so characteristic of an internal coma. However, here the process of decay and excitation of the described molecules continues in a quieter and smoother regime.
- Coma of atomic composition... It is also called ultraviolet. This region of the comet's atmosphere is observed in the Lyman-alpha hydrogen line in the distant ultraviolet spectral region.
Comet tail
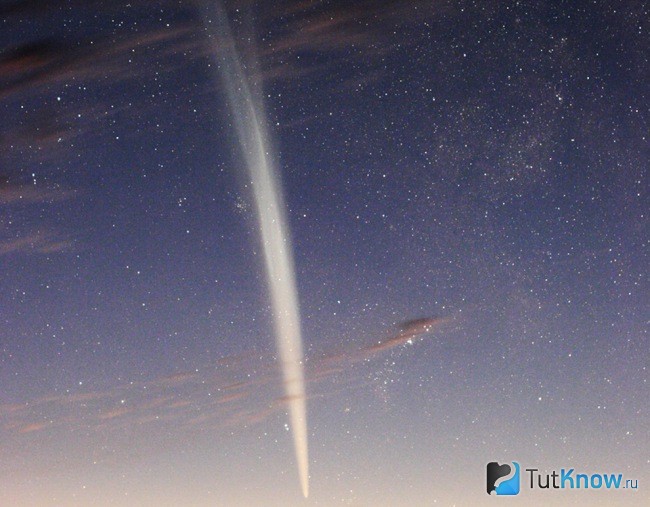

The comet's tail is a spectacle unique in its beauty and spectacularity. Usually it is directed from the Sun and looks like an elongated gas-dust plume. Such tails do not have clear boundaries, and we can say that their color gamut is close to full transparency.
Fedor Bredikhin proposed to classify sparkling plumes according to the following subspecies:
- Straight and narrow tails... These comet components have a direction from main star Solar system.
- Slightly deformed and wide-angle tails... These plumes deflect from the Sun.
- Short and highly deformed tails... This change is caused by a significant deviation from the main luminary of our system.
- Dust tail... A distinctive visual feature of this element is that its glow has a characteristic reddish tint. A train of this format is homogeneous in structure, stretching for a million, or even ten million kilometers. It was formed due to numerous grains of dust, which the energy of the Sun threw over a long distance. The yellow tint of the tail is due to the scattering of dust particles by sunlight.
- Plasma structure tail... This plume is much more extensive than the dust one, because its length is calculated in tens, and sometimes hundreds of millions of kilometers. The comet interacts with the solar wind, from which a similar phenomenon occurs. As you know, solar vortex flows are penetrated big amount fields of the magnetic nature of education. They, in turn, collide with the comet's plasma, which leads to the creation of a pair of regions with diametrically different polarities. From time to time there is a spectacular break of this tail and the formation of a new one, which looks very impressive.
- Anti-tail... It appears in a different way. The reason is that it is directed towards the sunny side. The influence of the solar wind on such a phenomenon is extremely small, because the plume contains large dust particles. It is possible to observe such an anti-tail only when the Earth crosses the comet's orbital plane. The disc-shaped formation surrounds the celestial body from almost all sides.
The main types of comets

The types of comets can be distinguished by the time of their revolution around the Sun:
- Short-period comets... The orbital time of such a comet does not exceed 200 years. At the maximum distance from the Sun, they have no tails, but only a barely perceptible coma. With a periodic approach to the main luminary, a plume appears. More than four hundred such comets have been recorded, among which there are short-period celestial bodies with a term of 3-10 years around the Sun.
- Comets with a long orbital period... The Oort cloud, according to scientists, periodically supplies such space guests. The orbital term of these phenomena exceeds the mark of two hundred years, which makes the study of such objects more problematic. Two hundred and fifty such aliens give reason to assert that in fact there are millions of them. Not all of them are so close to the main star of the system that it becomes possible to observe their activity.
The most famous comets of the solar system
There are a large number of comets that pass through the solar system. But there are the most famous cosmic bodies that are worth talking about.
Halley's comet
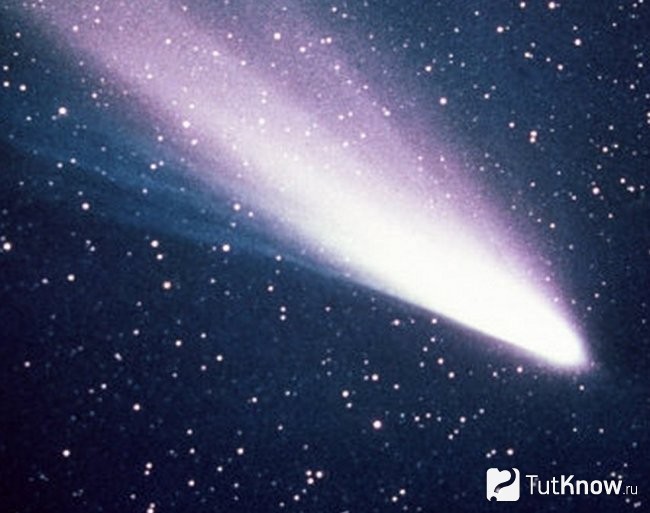

Halley's comet became famous thanks to the observations of it by the famous researcher, after whom it got its name. It can be attributed to short-period bodies, because its return to the main luminary is calculated as a period of 75 years. It is worth noting the change in this indicator towards parameters that fluctuate within 74-79 years. Its celebrity lies in the fact that it is the first celestial body of this type, the orbit of which it was possible to calculate.
Certainly, some long-period comets are more spectacular, but 1P / Halley can be observed even with the naked eye. This factor makes this phenomenon unique and popular. Almost thirty recorded appearances of this comet delighted outside observers. Their periodicity directly depends on the gravitational influence of large planets on the life of the described object.
The speed of Halley's comet in relation to our planet is striking, because it exceeds all indicators of the activity of the celestial bodies of the solar system. The approach of the Earth's orbital system with the orbit of the comet can be observed at two points. This results in two dusty formations, which in turn form meteor showers called Aquarids and Oreanids.
If we consider the structure of such a body, then it differs little from other comets. When approaching the Sun, the formation of a sparkling plume is observed. The comet's nucleus is relatively small, which may indicate a pile of debris in the form of building material for the base of the object.
It will be possible to enjoy the extraordinary spectacle of the passage of Halley's comet in the summer of 2061. Better visibility of the grand phenomenon is promised compared to the more than modest visit in 1986.
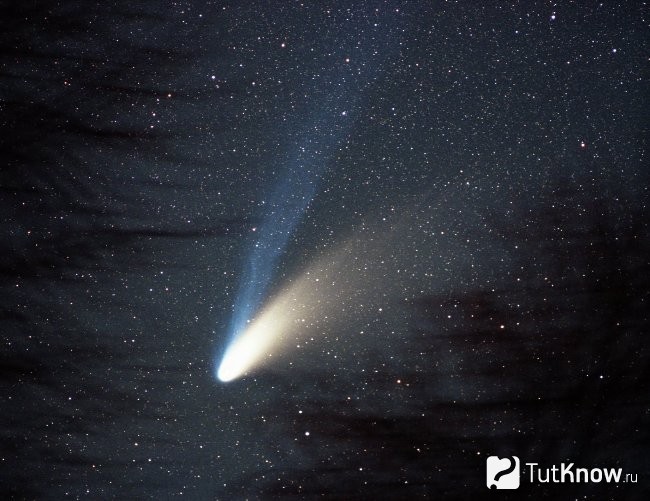

This is a fairly new discovery, which was made in July 1995. Two Space Explorers discovered this comet. Moreover, these scientists conducted separate searches from each other. There are many different opinions regarding the described body, but experts agree on the version that it is one of the brightest comets of the last century.
The phenomenality of this discovery lies in the fact that at the end of the 90s, the comet was observed without special devices for ten months, which in itself cannot but surprise.
The shell of the solid core of a celestial body is rather inhomogeneous. Ice-covered areas of unmixed gases are combined with carbon oxide and other natural elements. Finding minerals that are characteristic of the structure crust, and some meteorite formations once again confirm that Comet Hale-Bop originated within our system.
The influence of comets on the life of planet Earth

There are many hypotheses and assumptions regarding this relationship. There are some comparisons that are sensational.
Icelandic volcano Eyjafjallajokull began its active and destructive two-year activity, which surprised many scientists of that time. This happened almost immediately after the famous emperor Bonaparte saw the comet. This may be a coincidence, but there are other factors that make you wonder.
The previously described Halley's comet strangely influenced the activity of such volcanoes as Ruiz (Columbia), Taal (Philippines), Katmai (Alaska). The impact of this comet was felt by people living near the volcano Cossouin (Nicaragua), which began one of the most destructive activities of the millennium.
Comet Encke caused the most powerful eruption of the Krakatoa volcano. All this may depend on solar activity and the activities of comets, which provoke some nuclear reactions on their approach to our planet.
Falling comets are quite rare. However, some experts believe that the Tunguska meteorite belongs to just such bodies. They cite the following facts as arguments:
- A couple of days before the catastrophe, the appearance of dawns was observed, which, with their variegation, testified to anomality.
- The appearance of such a phenomenon as white nights, in places unusual for it, immediately after the fall of a celestial body.
- The absence of such an indicator of meteoriticity as the presence of a solid substance of this configuration.
What a comet looks like - watch the video:
The comets of the solar system is a fascinating topic that requires further study. Scientists all over the world, engaged in the study of the Cosmos, are trying to unravel the secrets that these heavenly bodies of amazing beauty and power carry.

Features of cough treatment with bear fat Bear fat use for children
Chewing food thoroughly is the cheapest way to lose weight
What happens if you swallow food, practically without chewing
Why do mammary glands hurt before menstruation?
How to remove quickly than whiten, treat facial skin at home