Non-metals, with the exception of inert (noble) gases, are fairly chemically active simple substances that interact with metals, other non-metals, and some also with complex substances (for example, combustion and chlorination of methane CH 4, combustion of ethanol C 2 H 5 OH). Having at the external energy level half and more than half of the electrons than they are contained in the completed external energy level, it is energetically more profitable for atoms of non-metallic elements to attach rather than give away electrons. Therefore, in reactions with metals, atoms of non-metallic elements attach electrons, and in reactions with non-metals form joint electrons there is no pair. To find out, before an atom, which common electron pairs in a molecule are displaced from two non-metallic elements, a number of electronegativity helps:
· Electrical negativity
electronegativity
Within the same period, with an increase in the serial number, the nonmetallic properties of chemical elements and their compounds intensify. Within the same subgroup, with an increase in the serial number, the nonmetallic properties of chemical elements and their compounds weaken.
 Non-metals are more common in nature than metals. The composition of the air includes: nitrogen, oxygen, inert gases. Sulfur forms deposits of native sulfur. Deposits of native sulfur in the Pre-Carpathian region are one of the largest in the world. There are deposits of graphite, diamonds are very rare. The industrial graphite deposit in Ukraine is the Avalivsk deposit, the raw materials of which are used by the Mariupol Graphite Plant. Deposits of rocks that may contain diamonds have been discovered in several regions of Ukraine (in particular, in the Zhytomyr region, in Volyn), but industrial deposits have not yet been discovered. Significantly more atoms of non-metallic elements form various complex substances, among which oxides and salts dominate.
Non-metals are more common in nature than metals. The composition of the air includes: nitrogen, oxygen, inert gases. Sulfur forms deposits of native sulfur. Deposits of native sulfur in the Pre-Carpathian region are one of the largest in the world. There are deposits of graphite, diamonds are very rare. The industrial graphite deposit in Ukraine is the Avalivsk deposit, the raw materials of which are used by the Mariupol Graphite Plant. Deposits of rocks that may contain diamonds have been discovered in several regions of Ukraine (in particular, in the Zhytomyr region, in Volyn), but industrial deposits have not yet been discovered. Significantly more atoms of non-metallic elements form various complex substances, among which oxides and salts dominate.
Knowledge control:
1. Characterize a subgroup of oxygen.
2. Record the general electronic configuration for the oxygen subgroup.
3. Compare the properties of oxygen and ozone.
4. What is the significance of the ozone layer for life on Earth.
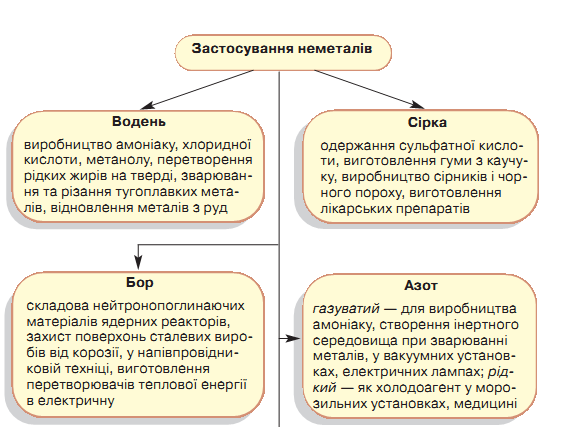
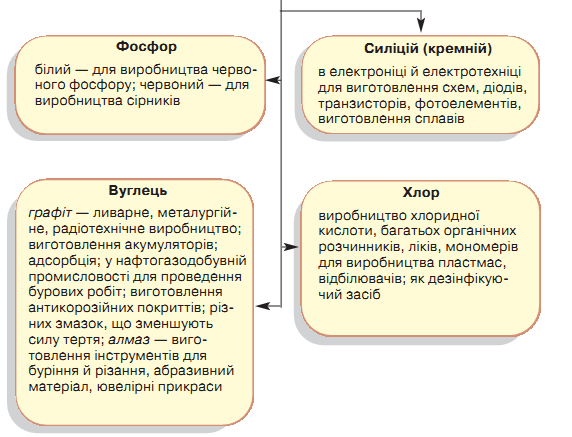
5. Treat non-metal applications.
Literature:

Srs 2
Topic: General information about mineral fertilizers. Nitrate content problems in food products. The role of chemistry in deciding the food program. Rational use of fertilizers and environmental problems when using mineral fertilizers.
Basic terms and concepts: fertilizers, mineral fertilizers, nitrates, micronutrient fertilizers, types of fertilizers and their use.
Plan:
1. The problem of nitrate content in foods.
3. The role of chemistry in solving the food problem.
Content:
1. The problem of nitrate content in foods.
For a person whose body weight is 60 kg, the maximum permissible daily rate nitrates is 0.76 mg per 1 kg of mass. Within permissible norms nitrates do not cause significant harm to human health.
However, the excessive use of nitrates as mineral fertilizers and the quality of food additives, which give meat products the color of natural meat, extend the shelf life of meat products and cheese, creates the risk of exceeding their maximum allowable standards daily consumption. The consequence of this may be toxic effect nitrates on the human body. It consists in the development of hypoxia - oxygen starvation of tissues, as well as the inhibition of the action of enzymes that catalyze the processes of tissue respiration. Symptoms of poisoning are nausea, vomiting, and blueness. skin body and oral mucosa appear 4-6 hours after eating foods high in nitrates. Particularly dangerous nitrates for the child's body.
Vegetables and milk contain much more nitrates than meat.
The measures to be taken to avoid poisoning with nitrates in food are:
1) compliance with the rules of agricultural technology for growing crops;
2) the consumption of water, milk, tested for the content of nitrates in them;
3) limited consumption of vegetables grown in greenhouses;
4) compliance with recommendations for reducing the nitrate content in the process of preparing vegetable dishes.
2. General information about mineral fertilizers. Rational use of fertilizers and environmental problems when using mineral fertilizers.
Substances, mainly salts containing nutrients necessary for plants, are called mineral fertilizers, they are introduced into the soil to increase its fertility in order to grow high and sustainable crops.
Elements such as Nitrogen, Potassium, Phosphorus come to them from the soil in the greatest quantity. Without Nitrogen, protein molecules cannot form; without Phosphorus, nucleic acids and vitamins. Thanks to Potassium, photosynthesis is accelerated, the accumulation of sucrose in sugar beets and starch in potatoes is improved, and the stalks of cereal plants are strengthened.
To restore the content of these elements in the soil in a natural way, it takes a long time, so without additional fertilizer yields from year to year inevitably decline. To prevent this, mineral and organic fertilizers are made and applied to the soil. It is estimated that in Ukraine 1 UAH., Spent on fertilizer production, gives an average of 2-3 UAH. arrived.
The main chemical elements necessary for the life of plants are (there are ten): C, O, H, M, P, K, Ca, Mg, Fe,
Elements of the mineral nutrition of plants, such as N. P, K, and some others, are necessary for plants in large doses. Therefore, they are called macroelements, and fertilizers containing them are called macro-fertilizers, or conventional fertilizers.
However, in addition to the above 10 elements, living organisms need very little large quantities (in macro amounts) such chemical elements as B, Cu, Co, Mn, Zn, Mo I.
They're called trace elements and fertilizers containing them - microfertilizers. Now it is impossible to do without micronutrient fertilizers - field vitamins, since their use opens up additional opportunities in the production of agricultural products.

Mineral fertilizers are divided into simple (one-sided) and complex (complex and mixed).
Simple fertilizers contain one nutrient. For example, sodium nitrate contains nitrogen, and potassium chloride contains potassium, etc.
Complex fertilizers in homogeneous particles contain two or more nutrients. For example, potassium nitrate contains potassium and nitrogen, nitrophoska contains nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc.
Mixed fertilizers are mechanical mixtures various kinds fertilizers - simple, complex or both. They are often called fertilizer mixtures. Mineral fertilizers are often called tukami, and industry produces them, - tukovoi. A powerful fertilizer industry was created in the Soviet Union. Nowadays, it produces more than 40 types of mineral fertilizers.
Nitrogen, phosphorus and potash fertilizers. Of greatest importance are nitrogen, phosphorus and potash fertilizers. Nitrogen fertilizers, as already noted, containing bound nitrogen. These are nitrate (sodium, potassium, calcium ammonium nitrates), ammonium salts, liquid ammonia, ammonia water, urea CO (NH 2) 2, (it is also used as a feed for livestock, contains more nitrogen - 47%), etc. Of these fertilizers are now the most widely used ammonium nitrate, i.e. ammonium nitrate. So that he does not lie down, he is released in a granular (granular) form.
Phosphate fertilizerare calcium and ammonium salts of phosphoric acid. They make up half of all mineral fertilizers produced. The most common phosphate fertilizers are:
Phosphorite flour, which is obtained by fine grinding of phosphorites. Since it contains a sparingly soluble salt of Ca 3 (PO 4) 2, it can be absorbed by plants only on acidic soils - podzolic and peaty. The assimilation is facilitated by the softness of the grinding, as well as its introduction into the soil together with acidic fertilizers, for example with (MH 4) 2 SO 4 or manure.
Simple superphosphate, which is obtained by treating apatites and phosphorites with sulfuric acid. The purpose of processing is to obtain soluble salt, which is well absorbed by plants in any soil:
The mixture of salts produced is usually called simple superphosphate; it is produced in very large quantities, both in granular form and in powder form. Granular fertilizer has several advantages compared to powder: it is easier to store (not caked); it is more convenient to apply to the soil with the help of fertilizer seeders, and most importantly - on most soils it gives a higher yield increase.
Dual superphosphate - concentrated phosphorus fertilizer composition Ca (H 2 PO 4) 2. In comparison with simple superphosphate does not contain ballast - Ca 8 O 4. The extraction of double superphosphate is carried out in two stages. Phosphoric acid is first mined. Then apatite or phosphorite is treated with an aqueous solution of phosphoric acid. The number of starting products is taken according to the equation:
Precipitate - concentrated phosphorus fertilizer composition CaNRO 4 2H? About. Slightly soluble in water, but soluble in organic acids. It is formed during the neutralization of phosphoric acid with a solution of calcium hydroxide:
Bone meal, which is obtained by processing the bones of domestic animals, contains Ca (PO 4) 2. Ammophos is a fertilizer containing phosphorus and nitrogen. It is formed when neutralizing phosphoric acid with ammonia. Usually contains salts of NH 4 H 2 PO 4 and (NH 4) 2 NRA 4. So, phosphoric fertilizers and calcium and ammonium salts of phosphoric acid.
Potash fertilizers are also necessary for plant nutrition. The lack of potassium in the soil significantly reduces the yield and resistance of plants to adverse conditions. Therefore, about 90% of the potassium salts that are mined are used as potash fertilizers.
3. The role of chemistry in solving the food problem.
Great attention devote to the production of mixed fertilizers containing trace elements. Currently, the production of food, in particular plant origin, worries all of humanity. Over the years, the sown area is becoming less and less, and the available ones are depleted on the content of nutrients. The rational use of fertilizers allows you to get out of this critical situation. In individual farms they mainly use organic fertilizer - humus, in collective - inorganic
In individual farms they mainly use organic fertilizer - humus, in collective farms - inorganic. Most often, fertilizers are applied to the soil during plowing, although root feeding is also practiced during the period of active vegetation.
Indoor plants are fed a solution of a specially selected mixture of fertilizers in spring and early summer.
For fertilizers to be most beneficial, you need to know when and which fertilizers are best used, which application method to choose, how to adjust the fertilizer application time to weather conditions, and much more. This is the subject of research in agrochemistry.
Most often, fertilizers are applied to the soil during plowing, although root feeding is also practiced during the period of active vegetation. Indoor plants are fed a solution of a specially selected mixture of fertilizers in spring and early summer. For fertilizers to be most beneficial, you need to know when and which fertilizers are best used, which application method to choose, how to adjust the fertilizer application time to weather conditions, and much more. This is the subject of research in agrochemistry.
Agrochemistry - a science that studies the interrelated chemical biological processes in soil and plants, reveals ways to increase crop yields.
Fundamental studies of plant nutrition and the use of fertilizers, which are generally recognized in agricultural chemistry and have received worldwide recognition, were carried out by Russian scientist D. M. Pryanishnikov. (Dmitry Nikolaevich Pryanishnikov (1865-1948) - author of more than 550 scientific papers). He was one of the organizers of the research institute, which is now called the D. M. Pryanishnikov Research Institute of Agrochemistry. He owns the theory of nitrogen nutrition of plants, the scheme for the conversion of nitrogen-containing substances in plants, the testing of various types of fertilizers in the main agricultural areas former USSR, in particular Ukraine. The scientist investigated the liming of acidic soils.
Knowledge control:
1. How to determine the content of nitrates in food?
2. What is the role of chemistry in solving the food problem?
3. What is agrochemistry?
4. How are fertilizers classified?
Literature:

Non-metals in nature. In nature, there are native N2 and O2 non-metals (in air), sulfur (in the earth's crust), but more often non-metals in nature are in a chemically bound form. First of all, it is water and salts dissolved in it, then minerals and rocks (for example, various silicates, aluminosilicates, phosphates, borates, sulfates and carbonates). In terms of prevalence in the earth's crust, non-metals occupy a wide variety of places: from the three most common elements (O, Si, H) to very rare (As, Se, I, Te).
Slide 3 from presentation "Chemistry of non-metals". The size of the archive with the presentation is 1449 KB.Chemistry Grade 9
summary of other presentations"Chemistry of non-metals" - The chemical structure and properties of metals and non-metals. Allotropy of carbon. The position of metals in the Periodic system of chemical elements. Presentation of a chemistry lesson for grade 9. Non-metals in nature. Non-metals. Red phosphorus Subject: NON-METALS. Oxygen. M. Allotropy. Physical properties of non-metals. Diamond. Non-metals also include hydrogen H and inert gases. general characteristics and properties of non-metals.
“Non-Metals” - A NUMBER OF NON-METAL ELECTRIC NEGATIVITY. Solid Carbon Silicon. What explains the diversity of the aggregate state of non-metals. Lattice) Red phosphorus - white phosphorus (the structure of the molecule P2 and P4). Do you think there are more metals or non-metals in the table? Test. Non-metals. Examples: Diamond - graphite (crystal. Chemistry. Grade 9. Teacher Kuleshova S.E. Liquid Bromine. Allotropy. What are the most active and strong non-metals. Oxygen O2 and Ozone O3. Aggregate state. Gaseous Oxygen, hydrogen. Physical properties.
"Halogens chemistry" - The biological role of chlorine. The results of the study. Enzymes become active in an acidic environment at 37-38 ° C. The results of the study spread in nature. Participates in the formation of hydrochloric acid, metabolism, and tissue construction. Conclusions and recommendations. The biological role of bromine. Dissolution of sodium bromide in water Yellow precipitate AgBr ?. Targets and goals. Halogen discovery results. Prospects for the project. 2011, the village of Petropavlovsk.
"Alkadien chemistry" - Alkadienes with isolated double bonds. Central atom C-Sp3 hybridization. Chemistry lesson in grade 9 Teacher: Dvornichena L.V. Updating of previously acquired knowledge. Allen structure diagram. Alkadienes: structure, nomenclature, homologs, isomerism. A game. The extreme atom is C-Sp2 hybridization. Alkadienes with a cumulative arrangement of double bonds. The nomenclature of alkadienes. Conjugated alkadienes.
Chemical Equilibrium - Task 2: Write the kinetic equations for chemical reactions. Irreversible. Change in the forward and reverse reaction rates in the process of establishing chemical equilibrium. Chemical equilibrium. Vpr \u003d Vobr. Task 1: Write down the factors affecting the speed of chemical reactions. I variant hcl + O2? H2O + cl2. Chemical reactions. II option H2S + SO2? S + H2O. Reversible.
“Characterization of metals” - The use of metals in human life. Properties of metals. General characteristics. Good electrical conductivity. General characteristics of metals. Finding metals in nature. A kind of metal. Other metals corrode, but do not rust. Metals form one of the foundations of civilization on planet Earth. Rusting and corrosion of metals. Metals Work content: From medical preparationscontaining precious metals, the most common are lapis, protargol, etc.
TOPIC: “The most important compounds of metals and nonmetals in nature and human economic activity”
In the human body, there are 81 chemical elements out of 92 found in nature. The human body is 60% water, 34% is organic matter and 6% is inorganic.
The human body is a complex chemical laboratory. It is hard to imagine, but daily our well-being, mood and even appetite may depend on mineral substances. Vitamins are useless without them; synthesis and breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates are impossible.
For example, if a person’s weight is 70 kg, then it contains (in grams): calcium - 1700, potassium - 250, sodium - 70, magnesium - 42, iron - 5, zinc - 3.
It is obvious that metals are necessary for the cells of the human body for normal life. Both excess and lack of metals have a negative effect on the body, and some metals can have a toxic effect on it.
The role of chemical elements.
The earth's crust is composed of a relatively small number of chemical elements. About ½ of the mass of the earth's crust is oxygen. More than ¼ - on silicon. Only 18 elements; O, Si,AL, Fe, Ca, K, Mg, H, Ti, C, Cv, P, U, Mn, F, Ba, Na, K make up 99.8% of the mass of the earth's crust. Of these, 98% are accounted for 8 elements - these are O, Si,AL, Fe, Ca, K, Mg, Na. Whereas in living organisms 6 elements are O, S,C, P, N,N they account for 97.4% of the mass of organisms. These elements are called organogenes.
From a chemical point of view, the selection of elements during the formation of the organism is reduced to the selection of those that are capable of forming strong, but at the same time labile bonds. These bonds should be easily homolytic (O 2 --- O + O) and heterolytic (H 2 O \u003d\u003d O + 2H) rupture, as well as cyclization (6 C - O). That is why organogen number 1 in living matter is carbon. The oxygen and hydrogen atoms are much less labile, but they also form a stable environment for the compounds of the other elements - this is water, thereby ensuring the occurrence of redox processes. Atoms of non-metals (N, P, S) and metals (Fe, Cu,Mg) are distinguished by special lability in the formation of various chemical bonds. Such as Si and AL, which make up the majority of the earth’s crust in living organisms, play a secondary role. Now we give them a description.
The value of metals in living organisms?
Iron. Its content in the body. It is part of hemoglobin, is a cofactor of catalose, an enzyme that destroys hydrogen peroxide and protects cells from its damaging effects. With a lack of iron, nitrogen, fat and fat metabolism are disturbed, anemia develops. In plants, the disease is chlorosis - discoloration of the leaves. The daily iron requirement is about 12 mg.
Calcium need for adults 0.8 -1 g, for children 0.6 -0.9 g per day.
Calcium is the main component of bones. Calcium ions transmit excitation to muscle fiber, causing it to contract, increase the strength of heart contractions, increase the phagocytic function of leukocytes, activate the protective function of proteins, calcium affects vascular patency - without this element fats, lipids and cholesterol would settle on the walls of blood vessels and clog them . It helps to remove heavy metals from the body. Calcium ions provide a constant osmotic blood pressure. It promotes blood coagulation during wounds. In plants, it plays a large role in the work of stomata. The exchange of calcium and its entry into the bone is regulated by vitamin D.
With a lack of calcium, it is washed out of the bones, stones are formed in the bones. Nicotine, caffeine, alcohol are one of the reasons for the lack of calcium, because contribute to its intensive excretion of urine. A lack of calcium causes an increase in blood coagulability, a decrease in the absorption of zinc by bone cells, the appearance of osteoarthritis, cataracts, and blood pressure.
Potassium and sodium are elements of biocurrents. Is it so?
Potassium is involved in the formation of bone tissue, is involved in maintaining the normal permeability of the outer membranes, for the formation of a number of enzymes, to maintain heart rate, is involved in the work of nerve tissue. In the human body, up to 0.25g. Daily requirement 2-5g.
Sodium. Daily requirement 0.1-3.3 g. Sodium enters the inner and outer layer of the cell membrane for the emergence of an electric membrane biopotential.
With a lack of sodium, colic, convulsions, circulatory disorders, weakness, a decrease in pressure, and fainting can occur.
Metals necessary for human life?
Small amounts include Mn, Co, Ni, Cn,Zn, AL, Cv, Ux need ranges from 300 mg to 0.2 mg per day. Zinc is a part of enzymes. Content it in human body 2-3g. Used for the preparation of eye drops, skin ointments.
Manganese. Its content in the human body is 12-20 mg. Its deficiency affects the growth of long bones, muscle tone, and the formation of cartilage.
Cobalt. Content 4-10mg. It participates in the synthesis of muscle proteins, nerve fibers, the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, promotes the inclusion of an iron ion in the hemoglobin molecule. Promotes carbohydrate metabolism.
Nickel. Content 14mg. In small quantities, it activates digestive enzymes. A lot of it in tobacco smoke. In large quantities, it dulls the functioning of digestive enzymes, affects vision (keratins, kerato-conjunctivitis). Affects the work of hematopoietic organs.
Copper is involved in photosynthesis, is involved in the absorption of nitrogen. The copper content is 80 mg. Participates in tissue respiration, affects the formation of myelin, affects the metabolism of vitamins B 1 , C, F, as well as the assimilation of iodine. It is part of some enzymes. The role of aluminum has not been sufficiently studied. It is known that in the human body the most in the lungs (5.19 mg), in the bones (0.5 mg), in the brain (0.25 mg), in the kidneys (0.1 mg), in the blood (0.06 mg).
Heavy metals and why are they dangerous?
Heavy metals are able to combine protein quite firmly, thereby disrupting the functioning of enzymes.
Hg - energetically connects with groupsHs - focuses on the kidneys disrupts their work - swelling.
Cadmium - is delayed in the kidneys, liver, pancreas and thyroid, thereby disrupting their work.
Lead - causes severe poisoning, gum disease, kidney disease, nervous system.
Waist - gum disease, hair loss, disrupted work gastrointestinal tract, nervous system, kidneys.
Chromium - mainly through the respiratory organs of the MPC - 0.0001 mg / l. It combines with proteins containing iron, proteins of the liver, bone marrow, lungs, causing lung cancer and various allergies.
Chemical element nameBiological role in the cell
CARBON
Included in all substances: the skeleton of their carbon atoms forms their basis.
OXYGEN
For aerobic organisms, it serves as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration, providing the cell with energy.
HYDROGEN
Included in all organic substances of the cell. The largest amount is contained in the composition of water.
NITROGEN
It is a part of proteins, nucleic acids, amino acids and
nucleotides.
SULFUR
It is part of sulfur-containing amino acids, vitamins and enzymes.
PHOSPHORUS
Included in ATP of other nucleotides and nucleic acids. The composition of tooth enamel.
MAGNESIUM
Included in chloroform.
CALCIUM
Participates in blood coagulation, participates in the formation of bones and teeth, spines and skeletons of invertebrates.
ZINC
It is part of the enzymes involved in alcoholic fermentation, in the composition of insulin.
IRON
It is part of hemoglobin, myoglobin. The lenses and cornea are an active enzyme.
IODINE
It is part of thyroxine - a thyroid hormone.
FLUORINE
Included in tooth enamel.
POTASSIUM
SODIUM
Participates in nerve impulse. Supports osmotic pressure in cells

Equipment: wolf mask possible
ISO Recording with Astroburn Lite
When you constantly want to eat
Only plural nouns
Additional way for graphic and text files